
Risk Management, Internal Audits, And
ISO Standards Services
خدمات
الإستشارات والتدريب
التميٌّز المؤسسي
جائزة قطر للتميز الحكومي ونموذج التميز المؤسسي الأوروبي EFQM

دليل السياسات
يشمل دليل السياسات والإجراءات تصنيف الأقسام والوحدات الإدارية وتحليل العمليات وتوثيقها واعتمادها

التخطيط الإستراتيجي
بناء الخطط الإستراتيجية ومتابعتها وفقا لرؤية قطر الوطنية 2030

التدقيق الداخلي
النتائج والتوصيات وتحليل بهدف تصحيح حالات عدم المطابقة وتحسين الأداء في مختلف الأقسام والإدارات

معايير الأيزو المختلفة
التأهيل لشهادات ضبط الجودة العالمية ايزو ISO وغيرها من المعايير العالمية

إدارة المخاطر
بناء سجل إدارة المخاطر ومعالجتها من خلال نهج مركزي كليّ وليس بشكل مستقل داخل الوحدات
Magnus Management – Quality, Strategy, EFQM Excellence


ماجنس مانجمنت للإستشارات ذ.م.م
عن الشركة؟
ماجنس للإستشارات شركة استشارات إدارية تم تأسيسها عام 2017 في الدوحة - قطر، لتقديم خدمات الإستشارات والتدريب في مجال التخطيط الإستراتيجي والتميز المؤسسي ومعايير الأيزو المختلفة. بالإضافة إلى إدارة المخاطر والتدقيق الداخلي والعديد من الخدمات الإدارية والتطوير المختلفة التي تستهدف مساعدة الشركات في تطوير اعمالها وتبسيطها وتحقيق التميز المؤسسي وفق معايير ومتطلبات توجهات دولة قطر وزيادة فعالية العمليات وزيادة الإنتاجية.
إن السـعي المسـتمر لتطويـر القطـاع الحكومـي فـي دولـة قطـر لمواكبـة التسـارع الـذي يشـهده العالـم فـي المنافسـة علــى التحــول لإقتصــاد المعرفــة يحتــم علــى الجهــات الحكوميــة والخاصة الســير قدمــا لتقديــم خدمــات ذات جــودة عاليــة للمتعامليــن، والعمــل علــى تطويرهــا ورفــع مســتويات كفاءتهــا وفعاليتهــا فــي ظــل تزايــد الطلــب علــى الخدمــات الحكوميــة مــن كافــة شــرائح المجتمــع القطــري واختــلاف احتياجاتهــم وارتفــاع مســتويات توقعاتهــم.
إن الإلتزام بمعايير الأيزو يعني وجود منهجية علمية في عملية اتخاذ القرار وإيجاد ثقافة التحسين المستمر في المؤسسة، الأمر الذي يسهم في تعزيز جودة المنتجات والخدمات من خلال وضع معايير وإرشادات تساعد الشركات على تطبيق ممارسات أفضل في تصميم وتصنيع المنتجات وتقديم الخدمات. وتحسين رضا العملاء من خلال تقديم منتجات ذات جودة مضمونة وخدمات موثوقة وملتزمة بالمعايير الدولية.
Magnus Management – Quality, Strategy, EFQM Excellence


رؤيتنا
أن نسهم في دعم المؤسسات القطرية والعربية وتحقيق الاكتفاء العربي في مجال الإستشارت الإدارية
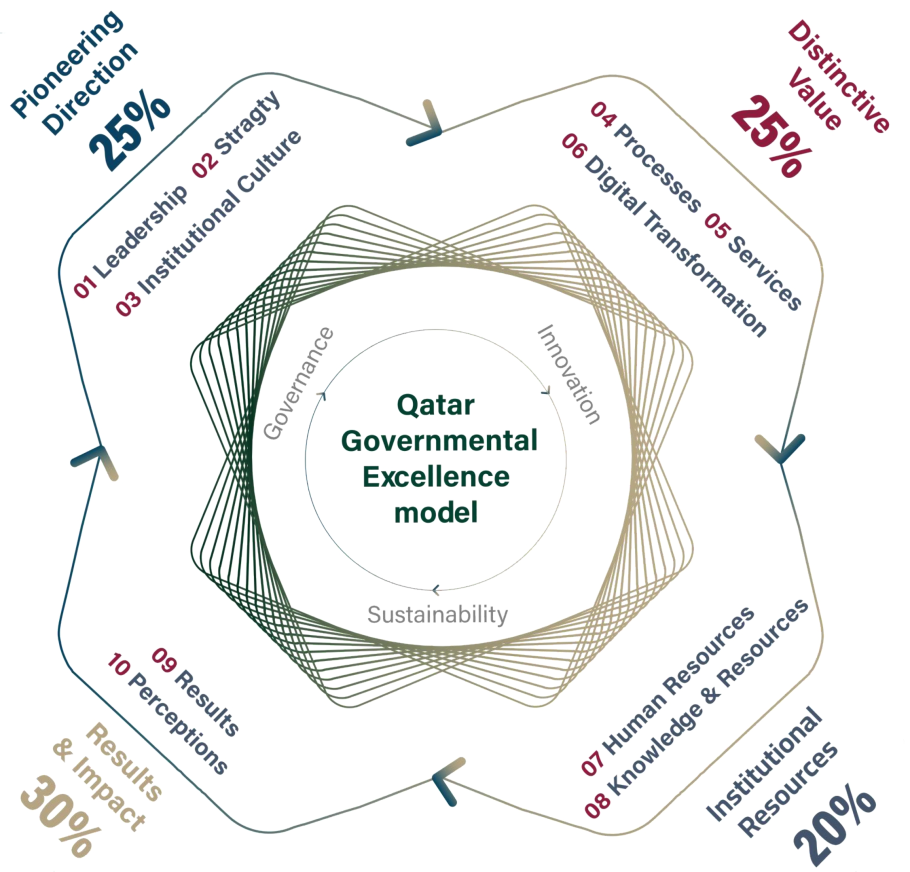
جائزة قطر للتميز الحكومي
أطلقت جائزةُ قطر للتميز الحكومي في أغسطس 2023، وذلك بهدف الارتقاء بمُستوى جودة الأداء الحكوميّ وتشجيع الجهات الحكومية والموظّفين على التنافس في تطبيق الجودة والتطوير والتميز في الأداء، من خلال تكريم الإنجازات والجهود المتميزة لجميع الفئات المساهمة في تحقيق رؤية قطر 2030
التوجه الريادي
القيادة، الإستراتيجية والثقافة المؤسسية
القيمة النوعية
العمليات، الخدمات والتحول الرقمي
الموارد المؤسسية
الموارد البشرية، الموارد والمعرفة
النتائج والأثر
النتائج والانطباعات

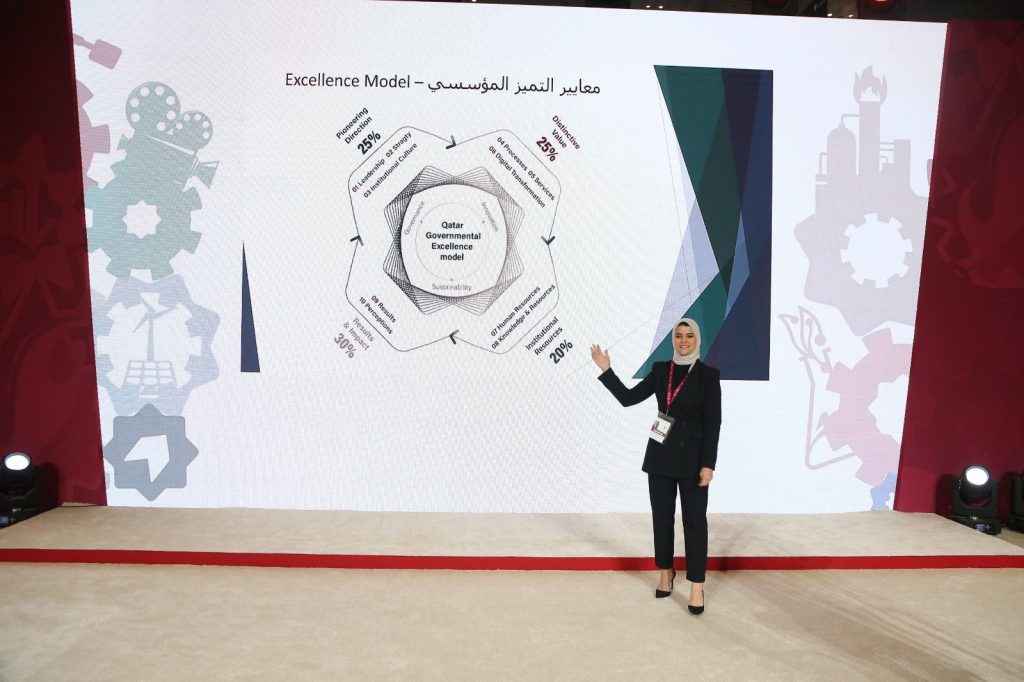
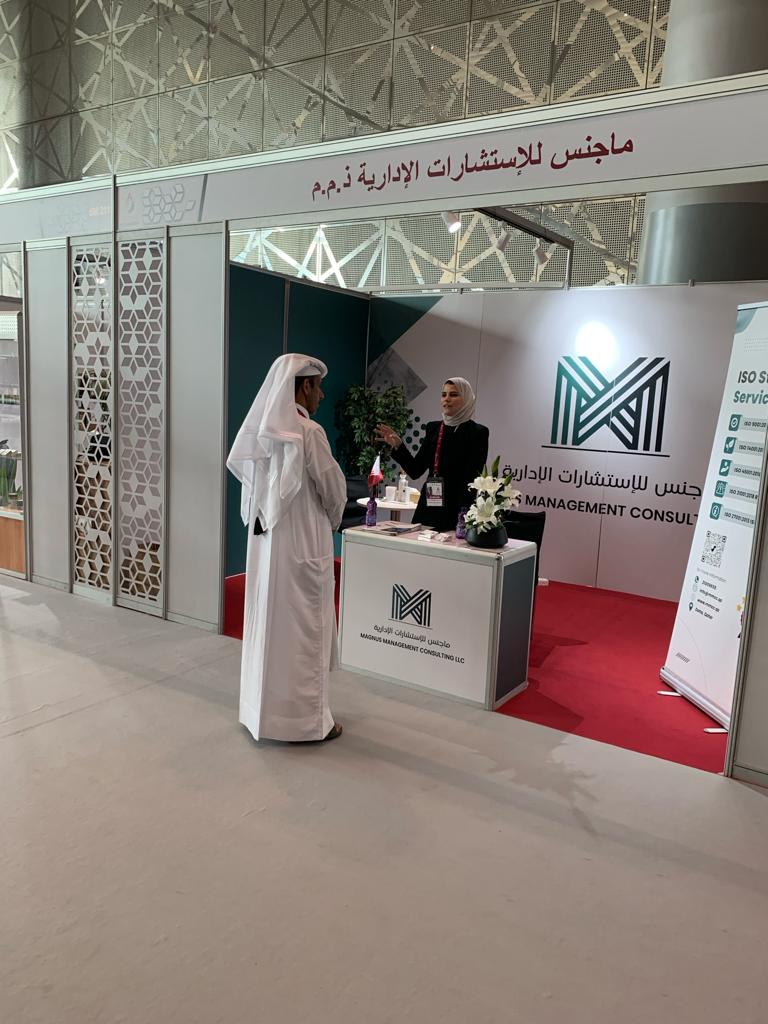
معرض صنع في قطر 2023


قامت ماجنس مانجمنت للإستشارات ذ.م.م بعقد ندوة تعريفية عن التميز المؤسسي والجودة وجائزة قطر للتميز الحكومي خلال مشاركتنا في معرض صنع في قطر لعام 2023 في الدوحة تم خلال الندوة عرض محاور جائزة قطر للتميز الحكومي ومعاييرها ومناقشة أهمية الالتزام بمعايير الأيزو العالمية، ومناقشة أهم مواصفات الأيزو التي تتسابق مختلف الشركات للحصول عليها ودورنا في تقديم خدمات الإستشارات والتدريب لتأهيل عملائنا في الامتثال لها وتأهيلهم للحصول على شهادة الأيزو. وتم القيام بمناقشات تعريفية مع الزوار بهدف التوعية بأهمية معايير الأيزو والجودة كمعايير ال ISO 9001:2015 QMS, ISO 14001:2015 EMS,ISO45001:2018 OH&S





شهاداتنا
عملائنا السعداء
سعدنا بالعمل مع العديد من المؤسسات والهيئات الحكومية والخاصة وتقديم خدمات الإستشارات والتدريب في مجال التخطيط الإستراتيجي والتميز المؤسسي ومعايير الأيزو المختلفة. بالإضافة إلى إدارة المخاطر والتدقيق الداخلي والعديد من الخدمات الإدارية والتطوير المختلفة.






خبراتنا
نحن نمتلك
استشاريون معتمدون
مقيم من EFQM
نموذج التميز الأوروبي
المنظمة العالمية للتخطيط الاستراتيجي
الوحيدون في قطر
مدققون معتمدون لأنظمة الأيزو
لأنظمة ISO 9001, ISOO 14001, ISO 45001 & ISO 27001
مستعد؟ أبدأ رحلة تطوير أعمالك
نحن هنا لبدء مشروعك الجديد والانتهاء منه قريبًا
